RNN Language Model with LSTM, GRU
Date: 23.05.25
Writer: 9tailwolf : doryeon514@gm.gist.ac.kr
Introduction
Long Short Term Memory is called by LSTM, which transform of Recurenct Neural Network, RNN structure. To make result by the time, RNN structure suggested and it is proved that useful. And LSTM is a advenced RNN structure.
Recurenct Neural Network
Recurenct Neural Network(RNN) is a multiful input output nerual network. There is a various form. Following is a RNN forms with matched examples.
- Vanilla Structure(One to One)
- One to Many : Image to Sentence
- Many to One : Sentimental analyze of sentence
- Many to Many : Translate
And the vanilla structure of RNN is a neural input system with extra \(h_{t-1}\) argument. Following is a figure of RNN.
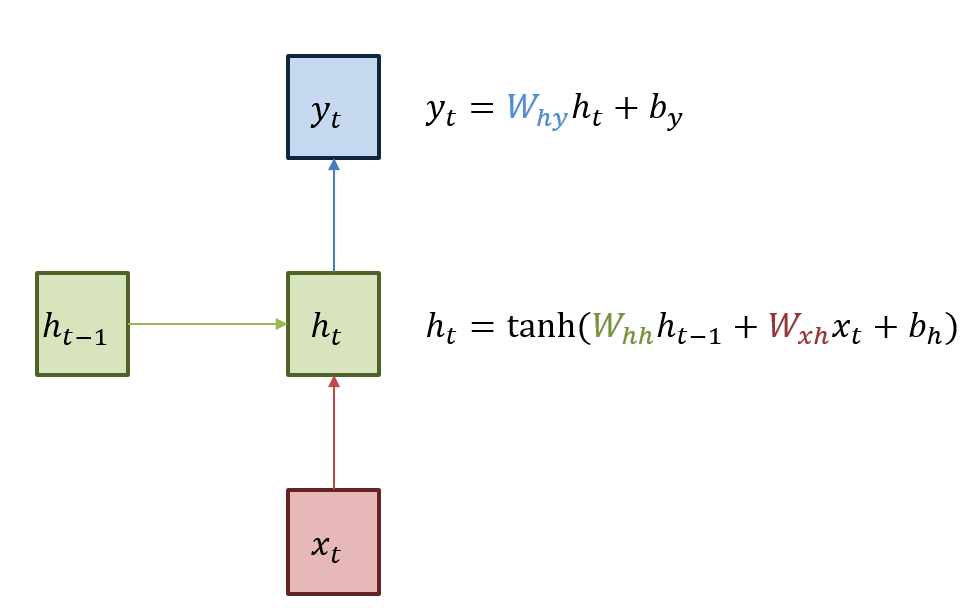
The characteristic of RNN is a \(h_{t}\), hidden layer can work continously. To calculate \(h_{t}\), we need input \(x_{t}\) with \(h_{t-1}\). And the next neural can recieve \(h_{t}\).
Normaly, to calculate \(h_{t}\), we use \(h_{t} = \tanh(W_{xh}x_{t} + W_{hh}h_{t-1} + b_{h})\) or \(h_{t} = \tanh(W_{h}[x_{t},h_{t-1}] + b_{h})\). And to calculate \(y_{t}\), we use some nonlinear function \(f\) like \(y_{t} = f(W_{hy}h_{t} + b_{y})\). And by backpropagation, we can determined coefficient.
Long Short Term Memory
RNN can represent multiful output with multiful inputs by recieve hidden layer data \(h_{t}\). But there is a downdsides. According to longer sequence, every data cannot recieve to far neural. To solve that problem, Long Short Term Memory is suggested. LSTM can send data by keeping important information with \(C_{t}\). Below is a Architecture of the LSTM.
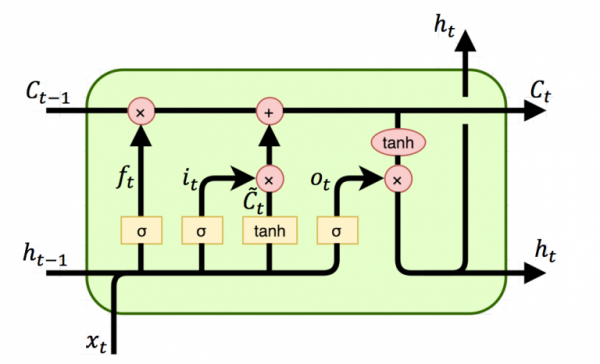
Forget Gate
\(f_{t}\) is called forget gate. It can calculate by \(f_{t} = \sigma(W_{f}[h_{t-1},x_{t-}] + b_{f})\).
Input Gate
\(i_{t}\) is called input gate. It can calculate by \(i_{t} = \sigma(W_{i}[h_{t-1},x_{t}] + b_{i})\).
Cell Gate
\(C_{t}\) is called Cell gate. It is consist of \(\tilde{C}_{t}\) and \(C_{t-1}\). First, \(\tilde{C}_{t}\) can calculate by following fomular. \(\tilde{C}_{t} = \tanh(W_{C}[h_{t-1},x_{t}] + b_{f})\). And by fomular \(C_{t} = f_{t} \centerdot C_{t-1} + i_{t} \centerdot \tilde{C}_{t}\), we can calculate \(C_{t}\).
Output Gate
\(o_{t}\) is called output gate. It can calculate by \(o_{t} = \sigma(W_{o}[h_{t-1},x_{t}] + b_{o})\).
Hidden Gate
\(h_{t}\) is called hidden gate. Finaly, it can calculate product, \(h_{t} = o_{t} \centerdot tanh(C_{t})\).
How can solve Vanishing Gradient Problem ?
Vanishing Gradient Problem is a problem with losing of past data. Too much nonlinear activation function cause a zero gradient and by this reason, updating of far data can disappear. In reallity, vanilla RNN has a vanishing gradient problem In Cell Gate, there is no nonlinear activative function.
Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory
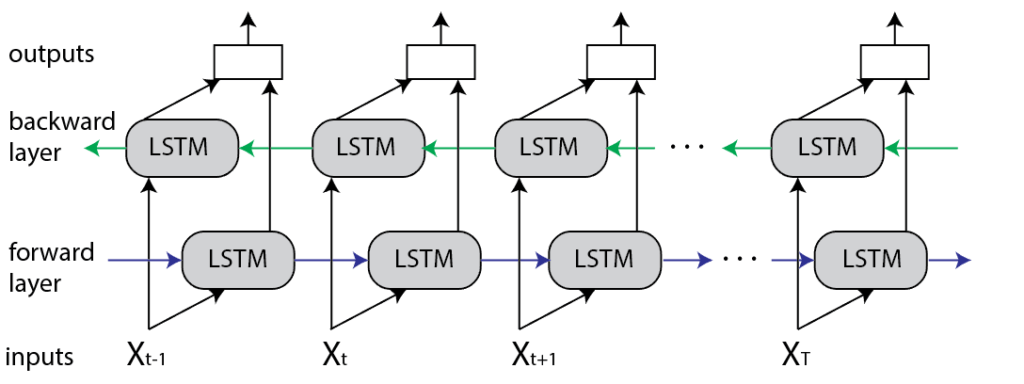
And above is a imporved version of LSTM, which is called Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory, or Bi LSTM. By appling bidirectional method, We can keep more information and can solve vanishing gradient problem.
Gate Recurrent Unit
At LSTM model, there is a overlapped computation. For example, forget gate, input gate, output gate overlappend. To solve that problem, we use Gate Recurrent Unit that is a simple LSTM model.
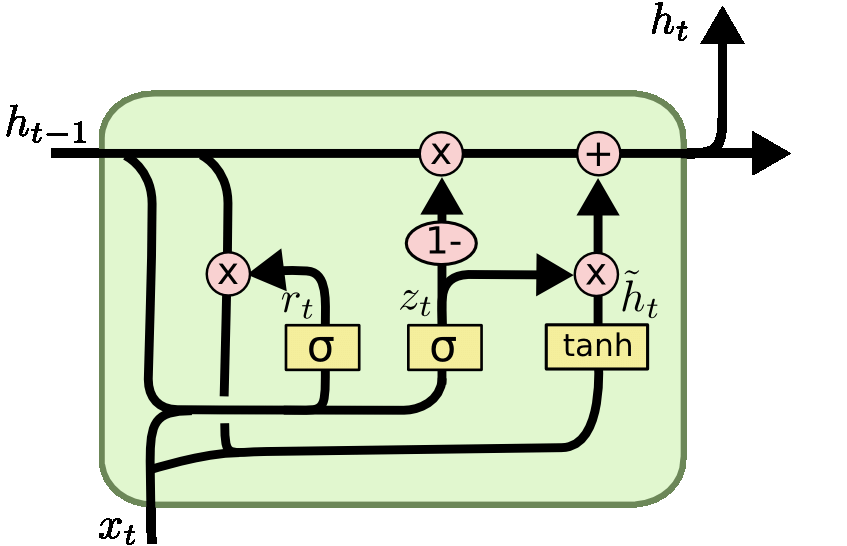
Reset Gate
\(r_{t}\) is called reset gate. It can calculate by \(r_{t} = \sigma(W_{f}[h_{t-1},x_{t-}] + b_{f})\).
Hidden Gate
\(h_{t}\) is called hidden gate. In GRU, hidden gate is consist of \(\tilde{h}_{t}\) and \(h_{t-1}\). At first, \(\tilde{h}_{t} = \tanh(W [r_{t} \centerdot h_{t-1}, x_{t}] + b)\). And next, we should calculate ratio of the \(\tilde{h}_{t}\) and \(h_{t-1}\). It is representated by \(z_{t} = \sigma(W_{z}[[h_{t-1},x_{t}]] + b_{z})\). Finaly, \(h_{t}\) can calculate following method. \(h_{t} = (1-z_{t})h_{t-1} + z_{t} \tilde{h}_{t}\).